How to Calculate Retained Earnings: Step-by-Step Guide
The retained earnings are the amount of profit earned by a company that is retained or reinvested in the business instead of being paid out in form of dividends to stockholders. Knowledge of retained earnings is important in determining the financial health and the growth of the company.
For business owners, investors, and financial analysts, knowing how to calculate retained earnings helps in making informed decisions about reinvestment, dividend policies, and long-term strategy.
The precise monitoring of retained earnings will help the companies to be able to expand, pay off their debt, or meet any unexpected costs, as well as give the stakeholders a clear understanding of the profitability and stability of the company over the long run.
What Are Retained Earnings?
The retained earnings are the profits a company keeps after covering the expenses and dividends. Retained earnings are in contrast to revenue, which is the amount of income received by the company as a result of sales that the company has retained to reinvest in the company or to settle its debt. They are determined by the formula:
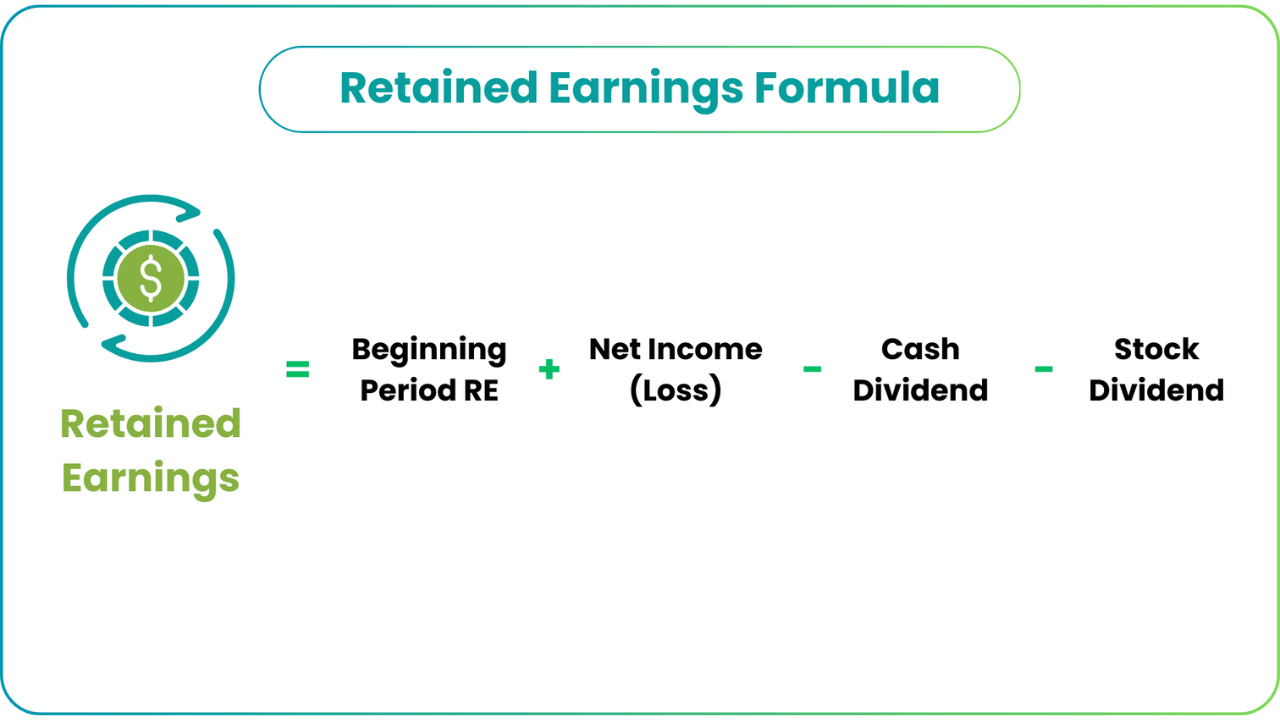
Retained Earnings = Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income – Dividends
This amount is reported in the shareholders equity under the balance sheet and it is one of the major financial indicators of financial health. An increasing balance of retained earnings would indicate that the firm is making a steady profit and reinvesting it back into the company and a decreasing balance would show that the firm is struggling to make money or paying out too much in dividends. Understanding how to calculate retained earnings is essential for assessing a company’s ability to fund future growth and manage financial obligations.
The Standard Formula for Retained Earnings
Formula:
Retained Earnings = Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income – Dividends
Components:
Starting Retained Earnings: This is the balance that has been left behind in the last period, and comprises the profits that have not been given out as dividends.
Net Income: The company has deducted its profit after the deductions of all expenses, taxes and costs. It shows the profitability of the company within the period.
Dividends: It makes payments to the shareholders based on the profits of the company. Such distributions lower the level of earnings held in the company.
Understanding how to calculate retained earnings is crucial for assessing a company’s financial health and its ability to reinvest in growth opportunities.
Step-by-Step Calculation Process
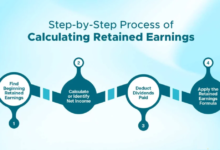
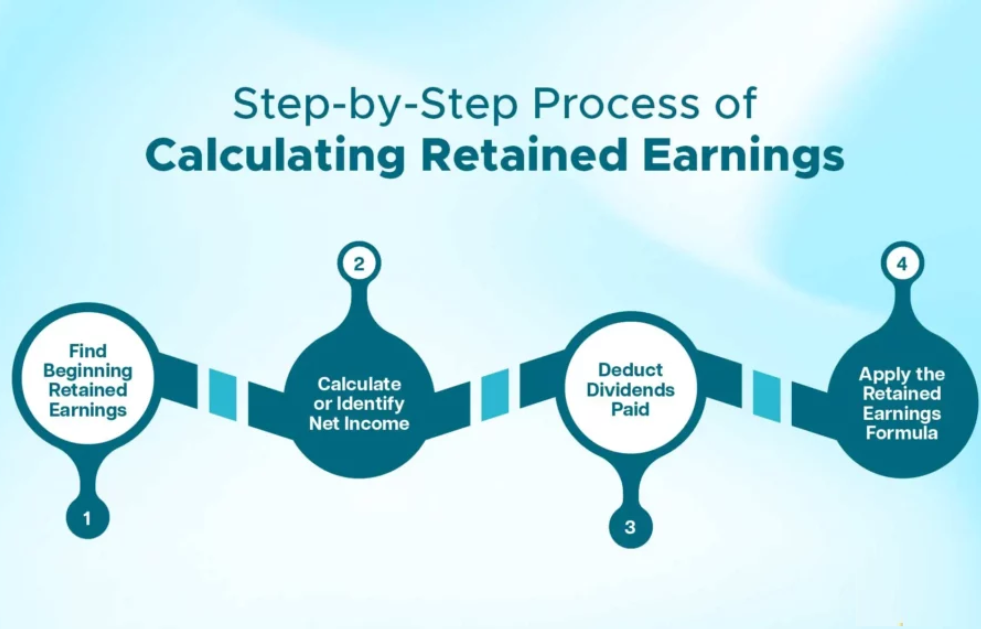
Step 1: Identify the Beginning Retained Earnings
Locate the retained earnings balance from the previous period’s balance sheet. This figure represents the cumulative profits retained in the company up to that point.
Step 2: Determine the Net Income
Obtain the net income from the current period’s income statement. Net income is the company’s total revenue minus expenses, taxes, and costs, indicating profitability.
Step 3: Subtract Any Dividends Paid
Review the company’s dividend records to find the total dividends distributed to shareholders during the period. Dividends reduce the amount of earnings retained in the business.
Step 4: Apply the Formula
Use the standard formula to calculate the ending retained earnings:
Retained Earnings = Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income – Dividends
This calculation provides the updated retained earnings balance, reflecting the company’s accumulated profits after accounting for dividends.
Example Calculation
Given:
- Beginning Retained Earnings: $100,000
- Net Income: $50,000
- Dividends Paid: $10,000
Calculation:
Ending Retained Earnings = Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income – Dividends Paid
Ending Retained Earnings = $100,000 + $50,000 – $10,000 = $140,000
This implies that the company will have retained earnings of $140,000 at the end of the period which can be utilized in reinvestment, payment of debts or other strategic projects.
Factors That Affect Retained Earnings
Net Income or Loss
Net income adds to retained earnings whereas net loss subtracts retained earnings. This is an indication of profitability of the company at the time.
Dividend Payments
Dividends decrease retained earnings. Dividends are payments made to shareholders whether in cash or stock that reduces the earnings held in the business.

Accounting Adjustments
Retained earnings can be affected by corrections or change of accounting policies. To illustrate, a balance may be inflated or deflated by making adjustments to the errors or changes in accounting estimates.
Importance of Retained Earnings in Business Strategy
1. Reinvesting in Business Operations
Retained earnings are an important internal source of funds and they allow firms to finance their operations without having to use external sources. This money may be used to increase working capital, improve equipment, or invest in research and development, which promotes innovation and efficiency of operation.
2. Paying Off Debts
The use of retained earnings to settle the outstanding debt makes the balance sheet of a company strong as it decreases the liabilities. This is a proactive measure that reduces interest payments as well as boosts financial stability and credit-worthiness.
3. Funding Expansion Projects
Businesses do not need to go to external capital sources to fund expansion programs like venturing into new markets, new products, or acquiring other companies; instead, they can use retained earnings to fund these expansion programs. This is a sustainable way of growing the business without losing control over the business.
Read Also: 5starsstocks.com AI Review: Is This AI Stock Picker Worth Your Investment?
Retained Earnings on the Balance Sheet
The retained earnings are recorded in the shareholders equity of the balance sheet. This part is the residual interest of the owners in the company after subtracting liabilities against assets. Retained earnings are the total value of the net income which has not been paid out to shareholders in the form of dividends.
The retained earnings reveal that the company has been profitable in the long-run and has decided to reinvest the profits into the business. An increasing retained earnings balance would indicate good reinvestment plans, which may translate to higher shareholder value. On the other hand, the decrease or negative retained earnings balance can be an indicator of financial difficulties or high dividend distributions.
Final Word
The correct calculation of the retained earnings is critical to the interpretation of the financial health and the prospects of a company in terms of its long-term growth. By knowing how to calculate retained earnings, business owners and investors can make informed decisions about reinvestment, dividend distribution, and debt management. Frequently checking the retained earnings will assist in tracking the trends, making the most efficient use of resources, and guaranteeing the development. By keeping up with this most important financial indicator, companies are able to stay afloat, streamline their strategy, and create shareholder value in the long-term.
Read More: Explore Coyyn.com Banking: Fast Transfers, Crypto Integration & More